Breast Cancer Treatment Options Early Signs and Prevention Tips
Breast cancer is one of the most prevalent types of cancer affecting women worldwide. It is essential to understand the early signs of breast cancer, the various treatment options available, and effective prevention strategies. This article aims to empower individuals with knowledge about breast cancer, focusing on symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures.
Understanding Breast Cancer Symptoms
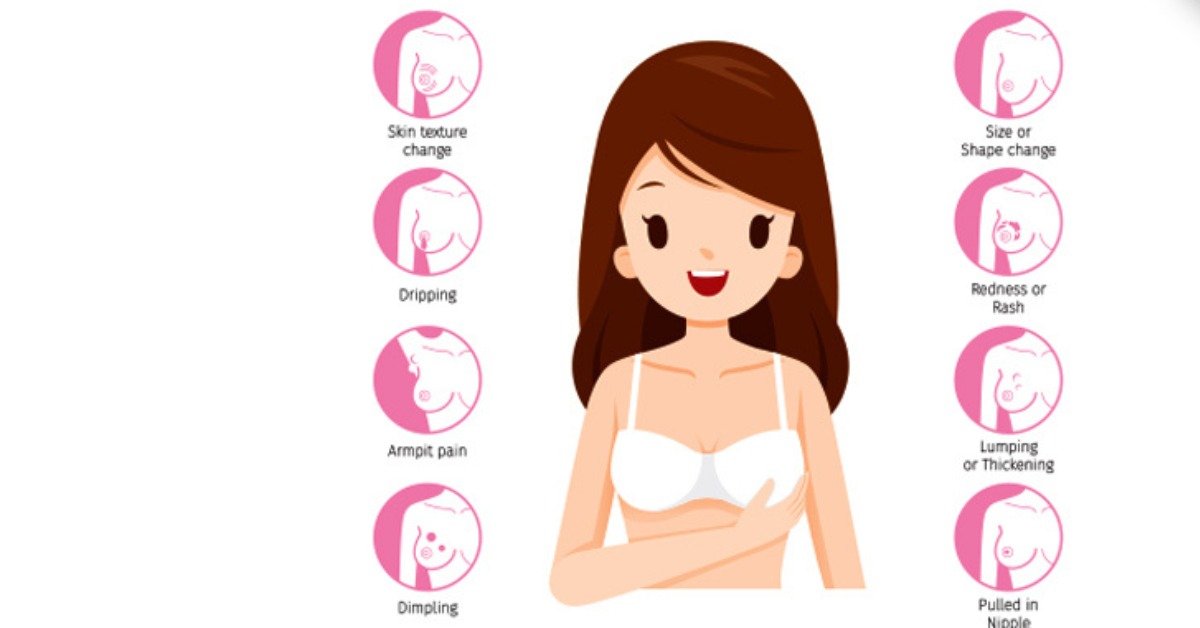
Early detection plays a crucial role in successful breast cancer treatment. Being aware of breast cancer symptoms can lead to prompt medical attention and better outcomes. Common breast cancer symptoms include:
A lump or mass in the breast or underarm: This is often the first noticeable sign. The lump may feel hard or different from surrounding tissue.
Changes in the size or shape of the breast: One breast may become noticeably larger or smaller than the other. Any sudden changes should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Skin changes: Look for any dimpling, puckering, or redness of the breast skin. These changes can indicate underlying issues.
Unexplained swelling or tenderness: If one breast feels swollen or tender, even without a lump, it is important to seek medical advice.
Nipple discharge: Any discharge from the nipple, especially if it is bloody or clear and not related to breastfeeding, should be examined.
If you notice any of these breast cancer symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional as soon as possible. Early intervention can significantly improve treatment success rates.
Breast Cancer Treatment Options
Once a diagnosis of breast cancer is confirmed, various treatment options may be considered. The choice of treatment is influenced by the stage of cancer, the specific characteristics of the tumor, and personal preferences. Here are the primary breast cancer treatment options:
Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of defense against breast cancer. The two most common surgical options are:
- Lumpectomy: This procedure involves removing the tumor along with a small margin of surrounding healthy tissue. It is often accompanied by radiation therapy to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
- Mastectomy: This surgery involves removing one or both breasts, depending on the cancer’s extent. There are several types of mastectomy, including total mastectomy and modified radical mastectomy, which may also involve the removal of lymph nodes.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays, similar to X-rays, to target and destroy cancer cells. It is commonly used after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence. Radiation can be administered externally or internally, depending on the specific case.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. This treatment can be administered before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink tumors or after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. Side effects may include nausea, fatigue, hair loss, and increased risk of infection, but many patients find it an effective treatment option.
Hormonal Therapy
Some breast cancers are hormone-sensitive, meaning they grow in response to hormones like estrogen. Hormonal therapy, such as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) or aromatase inhibitors, can be used to block these hormones from fueling cancer growth. This treatment can be particularly effective for postmenopausal women.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific characteristics of cancer cells. For instance, medications like trastuzumab (Herceptin) target the HER2 protein found in some breast cancers. This treatment approach is becoming increasingly popular due to its precision and reduced side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Effective Prevention Tips for Breast Cancer
While it is not possible to prevent all cases of breast cancer, certain lifestyle changes and preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk. Here are some effective tips:
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight, especially after menopause, is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, along with regular physical activity, can help manage weight and reduce risk.
Regular Screenings
Annual mammograms are essential for early detection. Women over the age of 40 should have regular screenings, and those with a family history or genetic predisposition may need to start screening earlier. Discuss personal risk factors with your healthcare provider to establish the best screening schedule.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Research indicates that alcohol consumption can increase breast cancer risk. Limiting intake to one drink per day or abstaining altogether can be a beneficial preventive measure.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking is associated with various cancers, including breast cancer. Quitting smoking not only lowers your cancer risk but also improves overall health.
Breast-Feed if Possible
Breastfeeding may lower the risk of breast cancer. If you can breastfeed your child, consider doing so for at least six months to provide health benefits for both you and your baby.
Genetic Testing and Counseling
For those with a family history of breast cancer, genetic testing can provide valuable insight. Knowing your genetic makeup can help guide prevention strategies and inform decisions about screenings and preventive surgeries.
Conclusion
Awareness of breast cancer symptoms, understanding treatment options, and adopting preventive measures are crucial steps in combating this disease. Recognizing early signs can lead to timely medical intervention and better treatment outcomes. Regular screenings and healthy lifestyle choices can significantly reduce the risk of breast cancer. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can take charge of their breast health and contribute to the fight against breast cancer.
